Climate Zones
Summary
Climates zones are regions are based on the long-term average weather pattern that are typically over a period of 30 years. These climate zones are bounded by location of latitude and altitude. Within each zone are terrain water bodies. The climate zones are around the poles. The sunlight rays reaches the earth at different angles at these zones. The sunlight rays determines the seasons as well. Climate zones can be seen on a map.
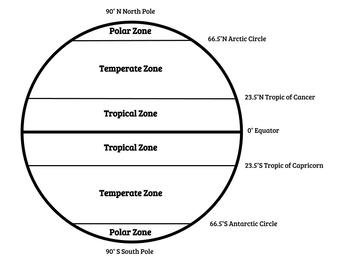

The Four Seasons of the Temperate Zone
This is “Four Seasons” song from Vivaldi. The song was also a poem.

Winter
During winter the trees sleep, they are brown and bare. Under the snow there are millions of seeds, each waiting for a little warmth and water to awaken it. Under the ground, beneath the snow, there are also some animals sleeping. These animals are waiting for warmth as well to come out. As the winter subside, the snow melt and soak into the ground. The grounds get soft and the seeds get wet.
Tiny plants burst out of the seed, and the roots pushes down. This is time for the hibernating animals to come out.
Spring
Spring is here when new plants poke out of the ground. The land turns green, the trees blossom, and this means there is now food for the animals. Animals that migrated returns. Spring is full of life as the days grow longer.
Summer
Soon summer will begin.The air grows warm; the leaves and flower petals begin to drop, and fruits begin to grow on the branches of trees. Summer is warm.

Autumn
As Autumn approaches, the flowers petals have all gone and there are lots of berries, nuts, and fruit. The seeds of the plants travel in the air or on animal’s fur. Some will be eaten by birds and animals. Autumn is the time for some animals to fatten themselves with seed and store some as well for the approaching winter. However, if the summer grows too warm, it could cause heat waves, or drought.
As the ground gets cold and hard, soon their will be no water for roots to find. Once again, the trees and some animals must sleep until spring comes around again. Yet, some other animals change their appearance to adapt to the coldness. Again it is winter.

The Earth’s Tilt Causes the Seasons
The amount of sunlight on any part of the earth is caused by the earth’s tilt. When the earth is at one end of its path around the sun, the North pole is tilted toward the sun and the south pole is tilted away from the sun. When most of the sun falls upon the northern half of the world, keeping it warm, this causes summer.
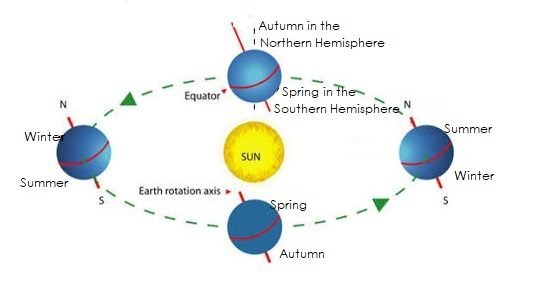
At the same time the southern half does not have much light, so it is cool. This causes winter. Once the earth makes a quarter turn around the sun, the amount of sun in the northern part is lighter, it is going into autumn; and the southern part is starting to get more light, so it is going into autumn.

The Two Seasons of the Tropics

In the tropics, there are just two seasons: the wet (or rainy) season and dry season. The weather in the tropics are controlled by the tropical rain belt. During the year, the tropical rain belt moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back again.

Rainy Season
During the rainy season the ground is soaked with water on many days. The grass is green and the streams and rivers are mostly swollen. Some animals retreat to higher grounds to avoid possible flooding. This is the period to expect tropical cyclones, street flooding, and river flooding. In between the rain there may be moments of dry spells (a short period of severe dry weather, less severe than a drought).
Sometimes the gusty winds are strong enough to through down trees or cause some damage to property. There may also be some landslide. However, the amount of rain varies from one area to another in the tropics. Some areas of the topics are wetter than other areas. Some are drier than other areas.



Dry Season
During the dry seasons, hot days are more frequent. The earth gets dry, bare and hot. The leaves fall to the ground and dry faster. Some water holes and rivers may dry up. There are frequent threats for forest fires. With infrequent rain, the collection of surface water may cause an increase in mosquito and mosquito-borne diseases. The lack of water causes some animals to migrate to more fertile spots. On an average month, precipitation is below 60 millimetres or 2.4 inches.

Activities:
Think of things people do during the wet and dry seasons. List the activities that take place in each season.
The Daily Cycle
Day and Night
The sun moves over the sky and reveals the blue sky. Soon it moves towards the horizon and silence and darkness sets in. This is day and night. You have seen this many times.


The Reason for Day and Night
The the sun does not move, but rather the world you live on is turning towards the sun. At one time half of the earth is covered with light from the sun and the other half is in darkness. No sunlight can fall on the dark side, until the earth turns.

The 24-hour Cycle
There is a 24-hour day/night pattern as a result of one full rotation of the earth around its own axis. This is referred to as diurnal cycle. This pattern is seen in the environment and in the climate. Our body also has an internal clock that affects our mood, mental alertness, hunger, and heart function.


Our biological clock is thrown off when we do things that are out of the ordinary.

We all have an internal body clock. It gives us the idea to sleep, relax, or eat. If you want to stay in the 24-hour cycle, your must ensure your brain get the sunlight it needs each day. We also must make sure we eat healthy foods in order to keep up with our internal body-clock.
See also:
Elementary Spanish Words for weather


















