Contents
Adjectives
An adjective is a describing word. It tells us more about a noun. Adjectives can be in colour and number.
There are three types of adjectives: descriptive, demonstrative, and quantitative adjectives.
Some adjectives describes a noun or a pronoun. They are called descriptive adjectives.
Example:
It is a lovely day today.
Some adjectives points out to something specific. They are called demonstrative adjectives.
Example:
I want that apple.
Some adjectives tell the exact number of something. It can tell “how many?” and “how much?” Such adjectives are called quantitative adjectives.
Example:
Mr. Bell has no money in his pocket. Some people are very poor.
Forming Adjectives
Adjectives are formed by adding “y” to a word, or dropping a “e” and adding “y”.
Example:
| salt | salty |
| stone | stony |
| sun | sunny |
Proper Adjectives
Proper adjectives are formed from a proper noun.
Example: We visited the Trinidad zoo.
Have you ever visited the Egyptian pyramids.
Note: Articles are adjectives. Indefinite articles, a and an are adjectives. Definite article, the, is an adjective.
Example:
I have a used computer.
I have the used computer.
Comparative and superlative adjectives
Sometimes we use a comparative adjective to compare the difference between things. Most comparative adjectives end in er.
Example: Jenny’s hair is darker than Patrice’s hair.
When we compare two nouns we use a comparative adjective.
When we compare more than two nouns we use a superlative adjective.
Example: Julia is tall. Luke is taller, but Matthew is the tallest.
Comparative adjectives often end with er. Superlative adjective often ends with est.
Note: When a single vowel precedes the last letter of an adjective, the last letter is doubled before “er” or “est” is added.
eg. wet – wetter; wettest
If the adjective ends with “y” change the “y” to an “i” before adding “er” or “est”.
e.g. pretty – prettier; prettiest
Some adjectives have two or more syllables. To form their comparative and superlative, add “more/less” or “most/least”
e.g.
- grateful – more grateful; most grateful
- comfortable – less comfortable; least comfortable
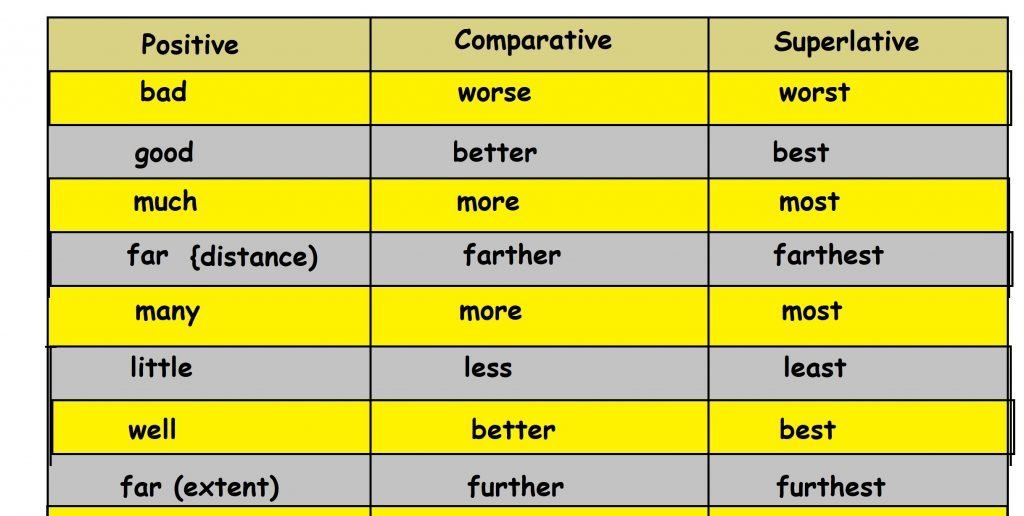
Finally there are irregular comparative and superlative forms of adjectives.
Adjectival Phrases
A phrase is usually a short group of words without a verb. A phrase does not make sense on its own. However, a phrase can tell us more about a noun; the job of an adjective. It is called an adjectival phrase.
Example: Martin fell down the long and winding stairs.
The phrase “long and winding” stairs tells us more about the noun stairs.
Adjectives (Similes)
A simile helps us to describe things better. It compares two things. Similes often contain adjectives.
Worksheets
Click the links below to download the following PDF worksheets.
Activity
Adjectives 1- This interactive activity helps you to effectively use descriptive adjectives in your writing.
Adjectives 2- This interactive activity helps you to use specific adjectives.
Click here to see more worksheets